Anterior branch of obturator nerve
| Anterior branch of obturator nerve | |
|---|---|
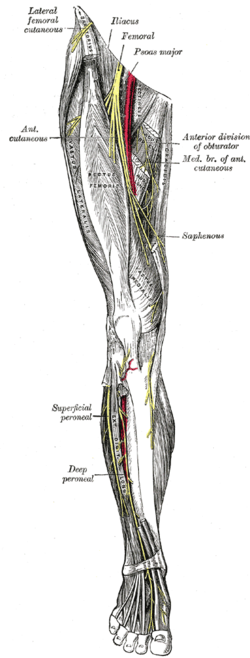 Nerves of the right leg seen from the front | |
| Details | |
| From | Obturator nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Ramus anterior nervi obturatorii |
| TA98 | A14.2.07.013 |
| TA2 | 6533 |
| FMA | 45306 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy [edit on Wikidata] | |
The anterior branch of the obturator nerve is a branch of the obturator nerve found in the pelvis and leg.[1]
It leaves the pelvis in front of the obturator externus and descends anterior to the adductor brevis, and posterior to the pectineus and adductor longus; at the lower border of the latter muscle it communicates with the anterior cutaneous and saphenous branches of the femoral nerve, forming a kind of plexus.
It then descends upon the femoral artery, to which it is finally distributed. Near the obturator foramen the nerve gives off an articular branch to the hip joint.
Behind the pectineus, it distributes branches to the adductor longus and gracilis, and usually to the adductor brevis, and in rare cases to the pectineus; it receives a communicating branch from the accessory obturator nerve when that nerve is present.
References
- ^ Choi, Eun Joo; Byun, Jong Min; Nahm, Francis Sahngun; Lee, Pyung Bok (September 2011). "Obturator Nerve Block with Botulinum Toxin Type B for Patient with Adductor Thigh Muscle Spasm -A Case Report-". Korean Journal of Pain. 24 (3): 164–168. doi:10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.164. PMC 3172331. PMID 21935496.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 954 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 954 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- medialthigh at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (medialthigh2)
- Anatomy photo:12:st-0602 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- v
- t
- e
| iliohypogastric | |
|---|---|
| ilioinguinal | |
| genitofemoral | |
| Lateral cutaneous | |
| obturator | |
| femoral |
| sciatic |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| other |
 | This neuroanatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e












