Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 3-Hydroxy-2-oxopropyl phosphate | |
| Other names Dihydroxyacetone phosphate DHAP | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.280 |
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C3H7O6P |
| Molar mass | 170.06 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  N verify (what is N verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP, also glycerone phosphate in older texts) is the anion with the formula HOCH2C(O)CH2OPO32-. This anion is involved in many metabolic pathways, including the Calvin cycle in plants and glycolysis.[1][2] It is the phosphate ester of dihydroxyacetone.
Role in glycolysis
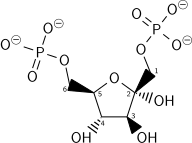
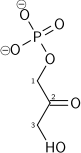
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate lies in the glycolysis metabolic pathway, and is one of the two products of breakdown of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, along with glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. It is rapidly and reversibly isomerised to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
| β-D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate | fructose-bisphosphate aldolase | D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate | dihydroxyacetone phosphate | ||
 |  | + |  | ||
 | |||||
Compound C05378 at KEGG Pathway Database. Enzyme 4.1.2.13 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00111 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00118 at KEGG Pathway Database.
The numbering of the carbon atoms indicates the fate of the carbons according to their position in fructose 6-phosphate.
| Dihydroxyacetone phosphate | triose phosphate isomerase | D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate | |
 |  | ||
 | |||
Compound C00111 at KEGG Pathway Database.Enzyme 5.3.1.1 at KEGG Pathway Database.Compound C00118 at KEGG Pathway Database.
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles.[§ 1]


- ^ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "GlycolysisGluconeogenesis_WP534".
Role in other pathways
In the Calvin cycle, DHAP is one of the products of the sixfold reduction of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate by NADPH. It is also used in the synthesis of sedoheptulose 1,7-bisphosphate and fructose 1,6-bisphosphate, both of which are used to reform ribulose 5-phosphate, the 'key' carbohydrate of the Calvin cycle.
DHAP is also the product of the dehydrogenation of L-glycerol-3-phosphate, which is part of the entry of glycerol (sourced from triglycerides) into the glycolytic pathway. Conversely, reduction of glycolysis-derived DHAP to L-glycerol-3-phosphate provides adipose cells with the activated glycerol backbone they require to synthesize new triglycerides. Both reactions are catalyzed by the enzyme glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase with NAD+/NADH as cofactor.
DHAP also has a role in the ether-lipid biosynthesis process in the protozoan parasite Leishmania mexicana.
DHAP is a precursor to 2-oxopropanal. This conversion is the basis of a potential biotechnological route to the commodity chemical 1,2-propanediol.[3]
See also
References
- ^ Berg, Jeremy M.; Tymoczko, Stryer (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W.H. Freeman and Company. ISBN 0-7167-3051-0.
- ^ Nelson, D. L.; Cox, M. M. "Lehninger, Principles of Biochemistry" 3rd Ed. Worth Publishing: New York, 2000. ISBN 1-57259-153-6.
- ^ Carl J. Sullivan, Anja Kuenz, Klaus‐Dieter Vorlop (2018). "Propanediols". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_163.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- v
- t
- e
Glucose-6-phosphate
isomerase

Fructose-bisphosphate
aldolase

Dihydroxyacetone phosphate

+
Triosephosphate
isomerase


Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenase




2 × Pyruvate