Retrovisceral space
| Retrovisceral space | |
|---|---|
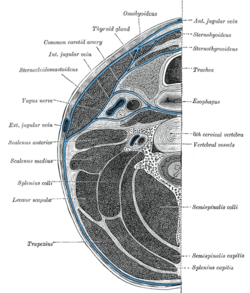 Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. Showing the arrangement of the fascia coli. | |
 Sagittal section of nose mouth, pharynx, and larynx. | |
| Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] |
The retrovisceral space is divided into the retropharyngeal space and the danger space by the alar fascia. It is of particular clinical importance because it is a main route by which oropharyngeal infections can spread into the mediastinum.
Some sources say the retrovisceral space is the same as the retropharyngeal space.[1]
Other sources say that the retrovisceral space is "continuous superiorly" with the retropharyngeal space.[2]
References
External links
- Thoracoscopic drainage with wound edge protector for descending necrotizing mediastinitis
- http://iris3.med.tufts.edu/headneck/spaces.htm
- v
- t
- e
Anatomy of the gastrointestinal tract, excluding the mouth
| Pharynx |
|
|---|---|
| Esophagus | |
| Stomach |
| Small intestine |
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large intestine |
|
 | This anatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e











