Styloglossus
| Styloglossus | |
|---|---|
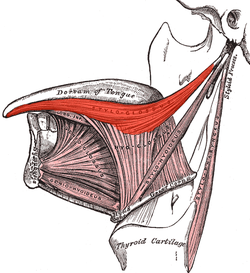 Extrinsic muscles of the tongue. Left side. (Styloglossus XII visible at center top.) | |
 Coronal section of tongue, showing intrinsic muscles. (Styloglossus labeled at center left.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Styloid process of temporal bone |
| Insertion | Tip and sides of tongue |
| Artery | Sublingual branch of the lingual artery |
| Nerve | Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) |
| Actions | Retraction and elevation of tongue |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus styloglossus |
| TA98 | A05.1.04.105 |
| TA2 | 2121 |
| FMA | 46692 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle [edit on Wikidata] | |
The styloglossus muscle is a bilaterally paired muscle of the tongue. It originates at the styloid process of the temporal bone. It inserts onto the side of the tongue. It acts to elevate and retract the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII).[1]
Anatomy
The styloglossus muscle is the shortest and smallest of the three styloid muscles.[citation needed]
Origin
It arises from (the anterior and lateral surfaces of) the styloid process of the temporal bone near its apex, and from the stylomandibular ligament.[citation needed]
Course and relations
It passes anterioinferiorly from its origin to its insertion between the internal carotid artery and the external carotid artery,[citation needed] and between the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle and the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle.[1]
Insertion
It divides upon the side of the tongue near the dorsal surface of the tongue, blending with the fibers of the longitudinalis inferior muscle anterior to the hyoglossus muscle.[citation needed]
Innervation
The styloglossus is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) (like all muscles of the tongue except palatoglossus which is innervated by the pharyngeal plexus of vagus nerve (CN X)).[citation needed]
Function
The styloglossus draws up the sides of the tongue to create a trough for swallowing. Acting bilaterally (both styloglossus muscles contracting simultaneously) they also aid in retracting the tongue.[citation needed]
Additional images
-
 Left temporal bone. Outer surface.
Left temporal bone. Outer surface. -
 Muscles of the neck. Anterior view.
Muscles of the neck. Anterior view. -
 The internal carotid and vertebral arteries. Right side.
The internal carotid and vertebral arteries. Right side. -
 Course and distribution of the glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves.
Course and distribution of the glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves. -
 Hypoglossal nerve, cervical plexus, and their branches.
Hypoglossal nerve, cervical plexus, and their branches. - Styloglossus muscle
- Styloglossus muscle
- Styloglossus muscle
- Styloglossus muscle
References
- ^ a b Morton, David A. (2019). The Big Picture: Gross Anatomy. K. Bo Foreman, Kurt H. Albertine (2nd ed.). New York. p. 252. ISBN 978-1-259-86264-9. OCLC 1044772257.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1130 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1130 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- "Anatomy diagram: 25420.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2015-02-26.
- v
- t
- e
- Oblique
- Rectus
- Levator palpebrae superioris
|
| Ear | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scalp/eyelid | |||||||
| Nose | |||||||
| Mouth |
| ||||||
- Veli palatini
- Musculus uvulae
- Palatopharyngeus
- Palatoglossus
| Extrinsic |
|
|---|---|
| Intrinsic |




















