ACVR2A
| ACVR2A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | ACVR2A, ACTRII, ACVR2, activin A receptor type 2A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 102581; MGI: 102806; HomoloGene: 20391; GeneCards: ACVR2A; OMA:ACVR2A - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Activin receptor type-2A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACVR2A gene.[5][6][7] ACVR2A is an activin type 2 receptor.
Function
This gene encodes activin A type II receptor. Activins are dimeric growth and differentiation factors which belong to the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) superfamily of structurally related signaling proteins. Activins signal through a heteromeric complex of receptor serine kinases which include at least two type I (I and IB) and two type II (II and IIB) receptors. These receptors are all transmembrane proteins, composed of a ligand-binding extracellular domain with cysteine-rich region, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain with predicted serine/threonine specificity. Type I receptors are essential for signaling; and type II receptors are required for binding ligands and for expression of type I receptors. Type I and II receptors form a stable complex after ligand binding, resulting in phosphorylation of type I receptors by type II receptors. Type II receptors are considered to be constitutively active kinases.[7]
Interactions
ACVR2A has been shown to interact with:
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000121989 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000052155 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Donaldson CJ, Mathews LS, Vale WW (May 1992). "Molecular cloning and binding properties of the human type II activin receptor". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 184 (1): 310–6. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(92)91194-U. PMID 1314589.
- ^ Bondestam J, Horelli-Kuitunen N, Hildén K, Ritvos O, Aaltonen J (April 2000). "Assignment of ACVR2 and ACVR2B the human activin receptor type II and IIB genes to chromosome bands 2q22.2-->q23.3 and 3p22 and the human follistatin gene (FST) to chromosome 5q11.2 by FISH". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 87 (3–4): 219–20. doi:10.1159/000015429. PMID 10702675. S2CID 36135054.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: ACVR2A activin A receptor, type IIA".
- ^ Lebrun JJ, Takabe K, Chen Y, Vale W (January 1999). "Roles of pathway-specific and inhibitory Smads in activin receptor signaling". Mol. Endocrinol. 13 (1): 15–23. doi:10.1210/mend.13.1.0218. PMID 9892009. S2CID 26825706.
- ^ De Winter JP, De Vries CJ, Van Achterberg TA, Ameerun RF, Feijen A, Sugino H, De Waele P, Huylebroeck D, Verschueren K, Van Den Eijden-Van Raaij AJ (May 1996). "Truncated activin type II receptors inhibit bioactivity by the formation of heteromeric complexes with activin type I. receptors". Exp. Cell Res. 224 (2): 323–34. doi:10.1006/excr.1996.0142. PMID 8612709.
- ^ Lewis KA, Gray PC, Blount AL, MacConell LA, Wiater E, Bilezikjian LM, Vale W (March 2000). "Betaglycan binds inhibin and can mediate functional antagonism of activin signalling". Nature. 404 (6776): 411–4. Bibcode:2000Natur.404..411L. doi:10.1038/35006129. PMID 10746731. S2CID 4393629.
- ^ Martens JW, de Winter JP, Timmerman MA, McLuskey A, van Schaik RH, Themmen AP, de Jong FH (July 1997). "Inhibin interferes with activin signaling at the level of the activin receptor complex in Chinese hamster ovary cells". Endocrinology. 138 (7): 2928–36. doi:10.1210/endo.138.7.5250. PMID 9202237.
- ^ Tsuchida K, Nakatani M, Matsuzaki T, Yamakawa N, Liu Z, Bao Y, Arai KY, Murakami T, Takehara Y, Kurisaki A, Sugino H (October 2004). "Novel factors in regulation of activin signaling". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 225 (1–2): 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2004.02.006. PMID 15451561. S2CID 34666659.
- ^ Matsuzaki T, Hanai S, Kishi H, Liu Z, Bao Y, Kikuchi A, Tsuchida K, Sugino H (May 2002). "Regulation of endocytosis of activin type II receptors by a novel PDZ protein through Ral/Ral-binding protein 1-dependent pathway". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (21): 19008–18. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112472200. PMID 11882656.
External links
- Human ACVR2A genome location and ACVR2A gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Welt CK (2002). "The physiology and pathophysiology of inhibin, activin and follistatin in female reproduction". Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 14 (3): 317–23. doi:10.1097/00001703-200206000-00012. PMID 12032389. S2CID 44327401.
- Matzuk MM, Bradley A (1992). "Cloning of the human activin receptor cDNA reveals high evolutionary conservation". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1130 (1): 105–8. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(92)90472-C. PMID 1311955.
- Mathews LS, Vale WW (1991). "Expression cloning of an activin receptor, a predicted transmembrane serine kinase". Cell. 65 (6): 973–82. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(91)90549-E. PMID 1646080. S2CID 36407277.
- Xu J, McKeehan K, Matsuzaki K, McKeehan WL (1995). "Inhibin antagonizes inhibition of liver cell growth by activin by a dominant-negative mechanism". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (11): 6308–13. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.11.6308. PMID 7890768.
- Attisano L, Cárcamo J, Ventura F, Weis FM, Massagué J, Wrana JL (1993). "Identification of human activin and TGF beta type I receptors that form heteromeric kinase complexes with type II receptors". Cell. 75 (4): 671–80. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90488-C. PMID 8242742. S2CID 25408172.
- Peng C, Huang TH, Jeung EB, Donaldson CJ, Vale WW, Leung PC (1993). "Expression of the type II activin receptor gene in the human placenta". Endocrinology. 133 (6): 3046–9. doi:10.1210/endo.133.6.8243335. PMID 8243335.
- De Winter JP, De Vries CJ, Van Achterberg TA, Ameerun RF, Feijen A, Sugino H, De Waele P, Huylebroeck D, Verschueren K, Van Den Eijden-Van Raaij AJ (1996). "Truncated activin type II receptors inhibit bioactivity by the formation of heteromeric complexes with activin type I. receptors". Exp. Cell Res. 224 (2): 323–34. doi:10.1006/excr.1996.0142. PMID 8612709.
- Attisano L, Wrana JL, Montalvo E, Massagué J (1996). "Activation of signalling by the activin receptor complex". Mol. Cell. Biol. 16 (3): 1066–73. doi:10.1128/mcb.16.3.1066. PMC 231089. PMID 8622651.
- Liu QY, Niranjan B, Gomes P, Gomm JJ, Davies D, Coombes RC, Buluwela L (1996). "Inhibitory effects of activin on the growth and morpholgenesis of primary and transformed mammary epithelial cells". Cancer Res. 56 (5): 1155–63. PMID 8640777.
- Nishitoh H, Ichijo H, Kimura M, Matsumoto T, Makishima F, Yamaguchi A, Yamashita H, Enomoto S, Miyazono K (1996). "Identification of type I and type II serine/threonine kinase receptors for growth/differentiation factor-5". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (35): 21345–52. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.35.21345. PMID 8702914.
- Lebrun JJ, Vale WW (1997). "Activin and inhibin have antagonistic effects on ligand-dependent heteromerization of the type I and type II activin receptors and human erythroid differentiation". Mol. Cell. Biol. 17 (3): 1682–91. doi:10.1128/mcb.17.3.1682. PMC 231893. PMID 9032295.
- Macías-Silva M, Hoodless PA, Tang SJ, Buchwald M, Wrana JL (1998). "Specific activation of Smad1 signaling pathways by the BMP7 type I receptor, ALK2". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (40): 25628–36. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.40.25628. PMID 9748228.
- Barbara NP, Wrana JL, Letarte M (1999). "Endoglin is an accessory protein that interacts with the signaling receptor complex of multiple members of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (2): 584–94. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.2.584. PMID 9872992.
- Lux A, Attisano L, Marchuk DA (1999). "Assignment of transforming growth factor beta1 and beta3 and a third new ligand to the type I receptor ALK-1". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (15): 9984–92. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.15.9984. PMID 10187774.
- D'Abronzo FH, Swearingen B, Klibanski A, Alexander JM (1999). "Mutational analysis of activin/transforming growth factor-beta type I and type II receptor kinases in human pituitary tumors". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84 (5): 1716–21. doi:10.1210/jcem.84.5.5704. PMID 10323406.
- Ebisawa T, Tada K, Kitajima I, Tojo K, Sampath TK, Kawabata M, Miyazono K, Imamura T (1999). "Characterization of bone morphogenetic protein-6 signaling pathways in osteoblast differentiation". J. Cell Sci. 112 (20): 3519–27. doi:10.1242/jcs.112.20.3519. PMID 10504300.
- van Schaik RH, Wierikx CD, Timmerman MA, Oomen MH, van Weerden WM, van der Kwast TH, van Steenbrugge GJ, de Jong FH (2000). "Variations in activin receptor, inhibin/activin subunit and follistatin mRNAs in human prostate tumour tissues". Br. J. Cancer. 82 (1): 112–7. doi:10.1054/bjoc.1999.0886. PMC 2363208. PMID 10638976.
- Shoji H, Tsuchida K, Kishi H, Yamakawa N, Matsuzaki T, Liu Z, Nakamura T, Sugino H (2000). "Identification and characterization of a PDZ protein that interacts with activin type II receptors". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (8): 5485–92. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.8.5485. PMID 10681527.
- v
- t
- e
-
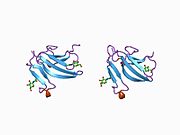 1bte: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR DOMAIN OF THE TYPE II ACTIVIN RECEPTOR
1bte: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE EXTRACELLULAR DOMAIN OF THE TYPE II ACTIVIN RECEPTOR -
 1lx5: Crystal Structure of the BMP7/ActRII Extracellular Domain Complex
1lx5: Crystal Structure of the BMP7/ActRII Extracellular Domain Complex -
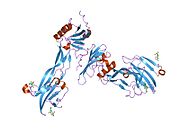 2goo: Ternary Complex of BMP-2 bound to BMPR-Ia-ECD and ActRII-ECD
2goo: Ternary Complex of BMP-2 bound to BMPR-Ia-ECD and ActRII-ECD






















